Nicolas Poussin was an influential figure in the French Baroque painting style. His exposure took him to the Italian city of Rome where he perfected his style. Evident from his paintings during his most productive years, his inspiration was drawn to religion and other classical mythologies.
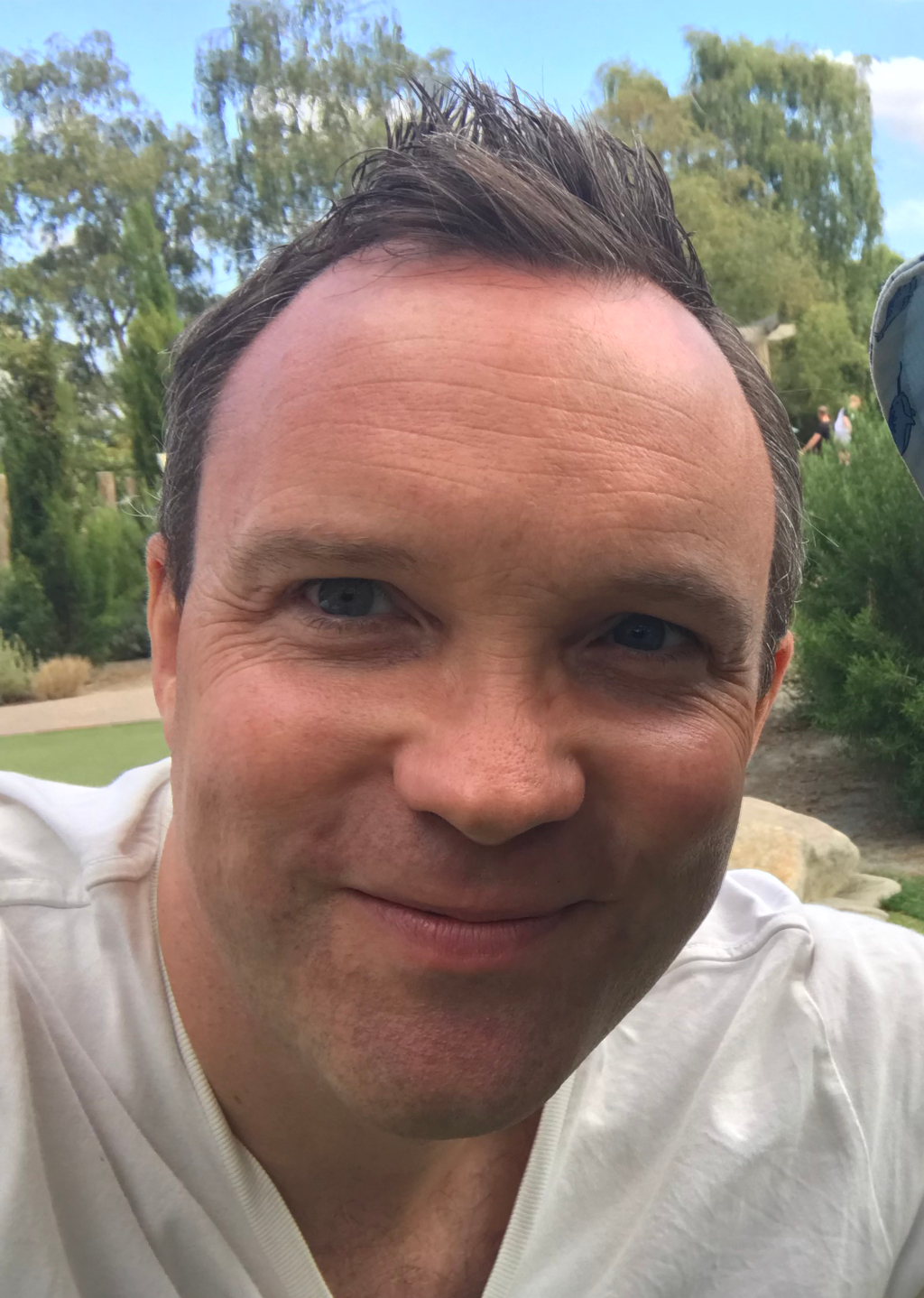
The Et in Arcadia ego (The Shepherd of Arcadia) was conceptualised from that association. It was done between 1637 and 1638 on canvas using oil. Canvas and oil were signature painting materials due to their durability and ease in painting. Done in Paris at the Musée du Louvre, the painting showed four people around a tomb. It is outdoor with two of the people carrying shepherd stick. They seem to be discussing something related to the tomb.
Poussin was inspired by Publius Maro's Eclogues. His painting on the tombs and its relationship with Arcadia in Greece gave Poussin a working theory. The same idea was also picked up by mid-15th century Italian painters. Arcadia was believed to be a place with tombs and mourning. Currently, the painting is housed at the Louvre in Paris.
The original painting measured 85 centimetres by 121 centimetres. There is another painting by Poussin on the same topic done 10 years earlier. It had the 4 people but were all actively reading the inscription on the tomb. However, the latter version was clearer, had bright colours and the character's facial impressions were vivid. His French routes and Italian connection made Nicolas Poussin a well-versed painter. The Et in Arcadia ego was his most visible painting, thanks to this heritage with the society and culture. His background as an early painter is not clear, but Marie de Medici was instrumental in his pupillage.
He went on to embrace what would later be termed as Classical Baroque style of painting which is associated with antiques, emotions, perfection and cultures. He grew into Raffaelo Sanzio da Urbino's mastery of the style and the influential Cardinal Francesco Barberini. This is where Poussin's love for religious settings cropped up. His works have greatly contributed to Jacques-Louis David, Paul Cezanne and Auguste Ingres' lives as painters in the 20th century. His legacy is still strong among the French artists from the 17th century onwards. His other popular works include the Abduction of the Sabine Women (1633-4), the Holy Family with St Elizabeth and John the Baptist (1655) and the Helios and Phaeton with Satum and the Four Seasons (1635).


 Nicolas Poussin.jpg)
