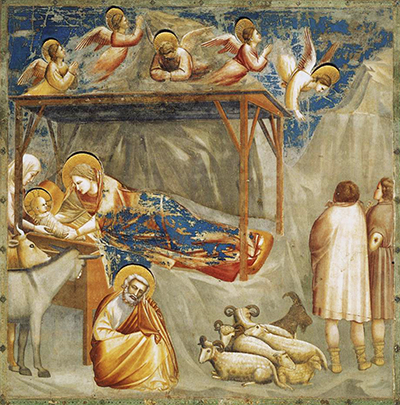
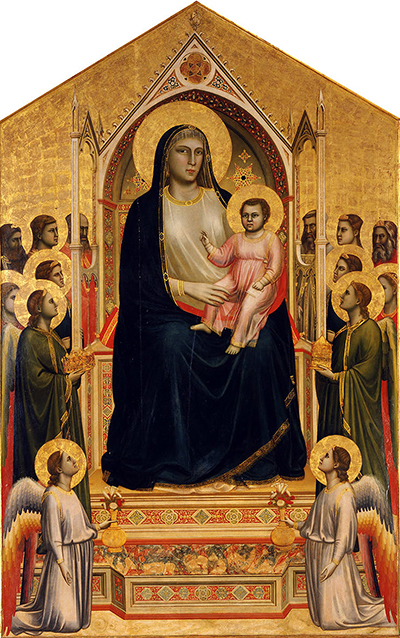
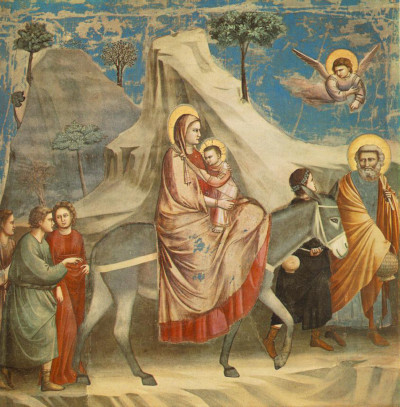
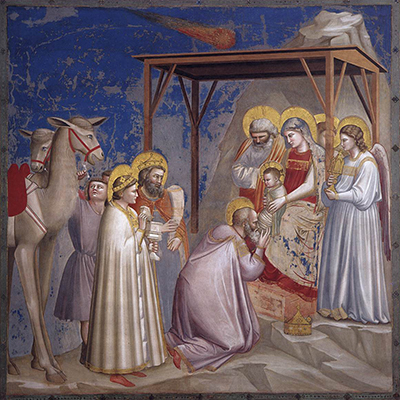
The Baroncelli Chapel in central Florence, Italy holds a collection of installed frescoes from some of the finest artists of the Italian Renaissance
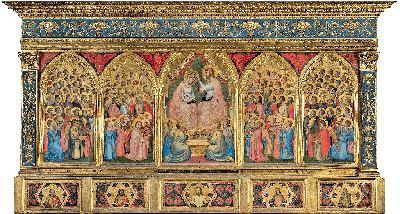
Giotto di Bondone is just one of a number of high profile artists who contributed to this stunning religious place of worship. Taddeo Gaddi (a pupil of Giotto), for example, completed a number of frescoes here between 1328 and 1338. The particular chapel can be found in the church of Santa Croce. Giotto's Baroncelli Polyptych was completed circa 1334 and can be considered the most famous artwork in this building.
A Polyptych is a general artistic term that refers to an artwork with many sides. Terms such as diptych and triptych are used to detail the specific number of sides. There would normally be a central panel which would hold the most significant painting in the series, with the side panels offering supporting artwork. The Early Renaissance was when such a format was seen most commonly and Giotto would himself produce several for commissioned projects in the Papal States. See also Piero della Francesca, Perugino, Carlo Crivelli and Lorenzo Lotto. They were also common in Northern Europe with the likes of Rogier van der Weyden, Jan van Eyck and Matthias Grünewald.
Uniquely, this is the only Giotto panel painting to remain in the place that it was first intended. The Baroncelli family commissioned the artist in 1327 to complete this artwork and they would then donate it to the chapel. One disadvantage of this fresco remaining in its original location is that it has not been preserved effectively and now resides in poor condition. Most religious venues do not have the sufficient funding to insure and preserve a historically significant painting.
More Renaissance Artists


 Giotto.jpg)
 Giotto.jpg)













